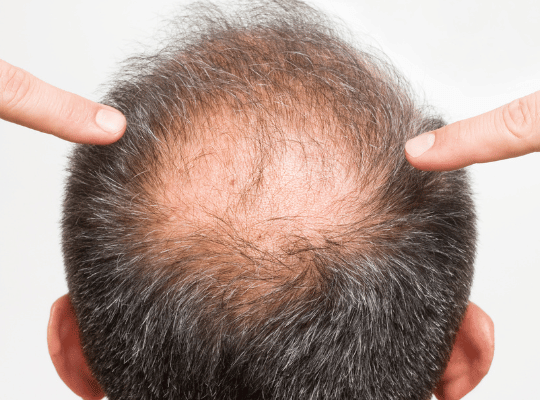
Have you ever wondered why some guys start losing their hair as they get older, while others keep their hair for a long time? The answer has a lot to do with something called testosterone and how it relates to hair loss. Hair loss, especially what’s known as male pattern baldness, is really common. In fact, by the time men turn 50, about half of them will have some level of hair loss. This type of hair loss is closely linked to testosterone levels in your body. But how exactly does testosterone cause hair loss, and what can you do about it? Let’s take a closer look at the connection, the types of hair loss related to testosterone, and the treatment options available.
The Science Behind Testosterone and Hair Loss
How Does Testosterone Affect Hair Growth?
Testosterone is a hormone that’s super important for things like building muscle and deepening your voice during puberty. But when it comes to hair, testosterone’s role is a bit tricky. The hormone itself doesn’t cause hair loss directly. The real problem starts when testosterone changes into another hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
What is Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)?
DHT is a stronger form of testosterone. It’s made when an enzyme in your body changes testosterone into DHT. DHT is important for some things, but it can be bad news for your hair. DHT attaches to hair follicles (the tiny holes in your skin where hair grows) and makes them shrink. This shrinking means that your hair becomes thinner and shorter, and eventually, the hair stops growing altogether.
Genetic Predisposition: Why Do Some People Lose Hair While Others Don’t?
The answer often lies in your genes. If baldness runs in your family, you’re more likely to experience it too. This is because your hair follicles might be more sensitive to DHT. So, even if your testosterone levels are normal, you could still lose hair if your hair follicles are easily affected by DHT.
Types of Hair Loss Related to Testosterone
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
The most common type of hair loss linked to testosterone is androgenetic alopecia, which is also called male pattern baldness. This type of hair loss usually starts with a receding hairline at the front or thinning hair on the top of the head. Over time, these bald areas can get bigger and join together, leading to more noticeable baldness.
Other Forms of Hormone-Influenced Hair Loss
Male pattern baldness is the most well-known type, but other kinds of hair loss can also be affected by hormones like testosterone. For example, telogen effluvium is when hair suddenly falls out due to stress or hormonal changes. This type of hair loss isn’t directly caused by testosterone, but hormonal imbalances that include testosterone can make it worse.
Signs and Symptoms
Early Signs of Testosterone-Related Hair Loss
One of the first signs that you might be losing hair because of testosterone is a receding hairline, especially around your temples. You might also notice thinning hair on the crown of your head. At first, the hair might just seem thinner and less dense, but as time goes on, you could see more obvious bald spots.
Progression Patterns of Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness usually follows a specific pattern. It often starts with thinning at the temples and on the crown. As the hairline keeps receding and the bald spot on the crown grows, these areas can eventually meet, leaving only a ring of hair around the sides and back of your head.
Diagnosis and Testing
How is Testosterone-Related Hair Loss Diagnosed?
To find out if your hair loss is related to testosterone, a doctor might use a few different methods. They might start with a physical exam and ask about your medical history. Sometimes, they’ll use a tool called a dermoscope to take a closer look at your scalp, or even do a scalp biopsy to check out the hair follicles under a microscope.
The Importance of Hormone Level Testing
Your doctor might also suggest checking your hormone levels with a blood test. This can help figure out if your testosterone or DHT levels are too high and causing your hair loss. Knowing your hormone levels can be really helpful in deciding what kind of treatment will work best for you.
Treatment Options
If you’re dealing with testosterone-related hair loss, there are several treatments you can try. Here’s a simple chart to compare some of the most common options:
| Treatment | How It Works | How Well It Works | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finasteride | Blocks DHT | Moderate to High | Might cause sexual side effects |
| Minoxidil | Widens blood vessels | Moderate | Could cause scalp irritation |
| Hair Transplantation | Moves hair follicles | High | Surgery risks like scarring |
| Low-Level Laser Therapy | Uses lasers to stimulate hair | Low to Moderate | Very few side effects |
Finasteride (DHT Blocker)
Finasteride is a prescription pill that works by blocking the enzyme that turns testosterone into DHT. This helps lower DHT levels, which can slow down hair loss and even help some hair grow back.
Minoxidil (Vasodilator)
Minoxidil is a liquid or foam that you put directly on your scalp. It helps by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, which can help some people regrow hair or slow down hair loss.
Hair Transplantation (Surgical Option)
If your hair loss is more advanced, you might consider hair transplantation. This surgery moves hair follicles from one part of your head to another. It’s a very effective way to restore hair, but it’s also the most expensive and involves surgery, which has risks.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-Level Laser Therapy uses special lasers to stimulate hair growth. It’s a safe option with few side effects, but it doesn’t work as well for everyone and may take a while to show results.
Lifestyle Factors and Prevention
Diet and Nutrition for Hair Health
Eating the right foods can help keep your hair healthy. Nutrients like biotin, zinc, and iron are important for hair growth. A balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains can support your hair and might help slow down hair loss.
Stress Management
Stress can make hair loss worse, especially if you’re already at risk for male pattern baldness. Managing stress through things like exercise, meditation, or talking to someone can help protect your hair.
Exercise and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels
Getting regular exercise is good for your health and helps keep your testosterone levels balanced. But be careful—too much intense exercise might actually lower your testosterone levels. So, it’s all about finding a good balance.
Future Research and Emerging Therapies
Ongoing Studies in Hair Loss Treatment
Scientists are always looking for new ways to treat hair loss. Some of the latest research includes things like gene therapy, stem cell treatments, and new medicines that target the hormonal causes of hair loss.
Potential New Approaches Targeting Testosterone-Related Hair Loss
Some new treatments being studied focus on stopping the process that makes hair follicles shrink when they’re exposed to DHT. These treatments are still being tested, but they could be more effective than current options in the future.
Conclusion
Understanding how testosterone affects hair loss can help you figure out what’s going on with your hair and what you can do about it. While male pattern baldness is common, and often tied to genetics and DHT levels, there are treatments available that might help you keep or regrow your hair. If you’re worried about hair loss, it’s a good idea to talk to a doctor who can give you personalized advice and help you choose the best treatment.
FAQs About Hair Loss and Testosterone
- Can taking testosterone supplements make me lose hair?
- Yes, taking testosterone supplements can increase DHT levels, which might lead to hair loss in people who are prone to male pattern baldness.
- Is hair loss from testosterone permanent?
- Hair loss from testosterone, especially from DHT, can sometimes be slowed down or even reversed with treatments, but it depends on the person.
- When does hair loss from testosterone usually start?
- Hair loss related to testosterone often starts in the late 20s to early 30s, but it can begin earlier or later depending on your genes.
- Can women lose hair because of testosterone?
- Yes, women can experience hair loss related to testosterone, especially if they have conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which affects hormone levels.
- Are there natural ways to lower DHT levels?
- Some natural methods, like eating a healthy diet, exercising, and taking certain supplements like saw palmetto, might help lower DHT levels, but more research is needed.